Title: Banish Back Pain for Good with These 5 Simple Movements
Chronic low back pain, impacting numerous Americans annually, often stems from sedentary lifestyles or excessive use. It may seem like you're damned if you sit, and damned if you move, but there's hope! Treatment options abound, including medications, surgery, and the most sustainable solution: regular back-strengthening exercises.
These simple movements, when practiced regularly, help prevent muscle weakness due to inactivity and improve your body's tolerance for physical activity as you age. The essential muscle groups to target are your back extensors and deep core stabilizers, abs, and glutes, along with the upper leg muscles.
Here are five exercises to keep your back healthy:

5 Powerful Exercises to Conquer Back Pain
Perform these moves virtually anywhere to strengthen your back and core. The American College of Sports Medicine suggests practicing functional training like these exercises 'two to three times per week, for 20 to 30 minutes' per session.

Attempt the routine below, repeating each exercise 2 to 4 times, and focus on proper form during every movement for optimal results:
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing
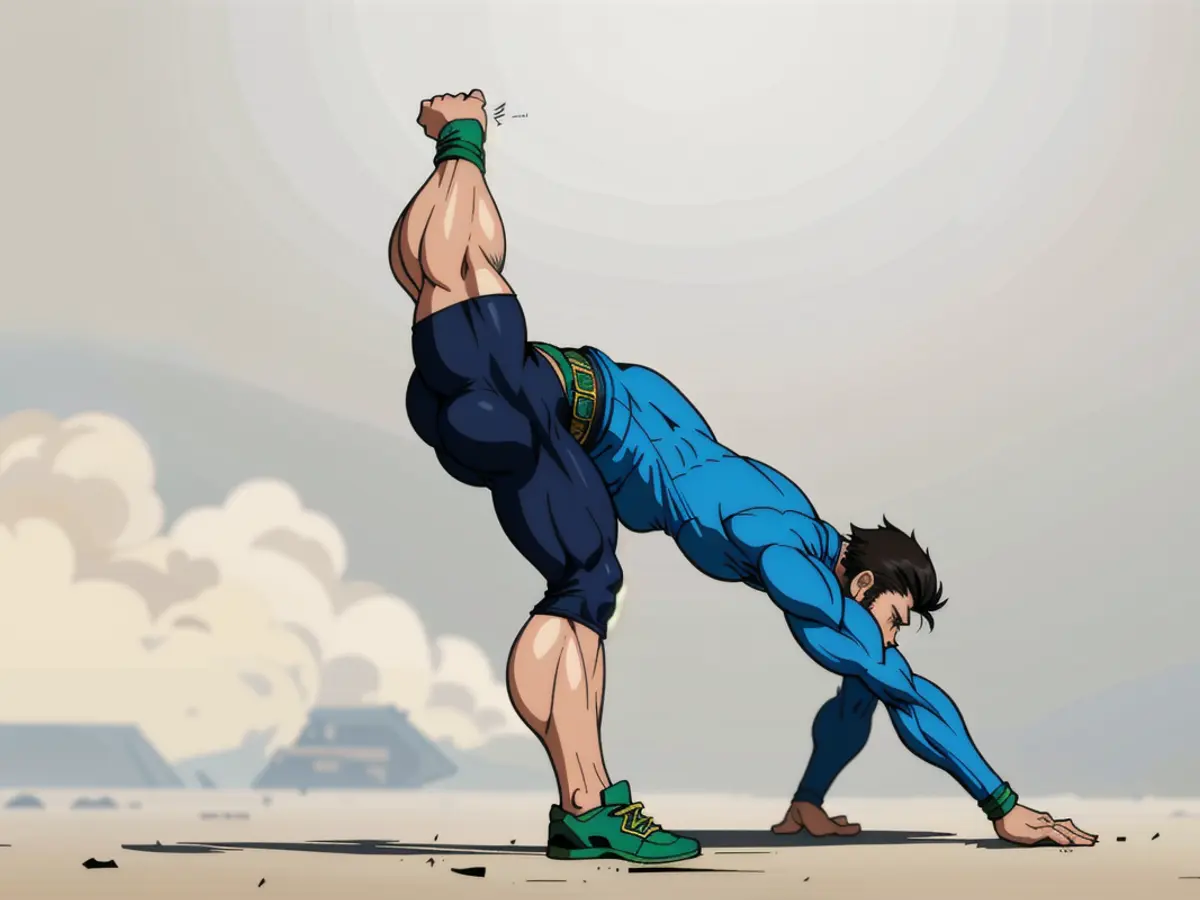

Optimize your oxygen intake and enhance spine strength with this breath-focused move.
Stand with your feet together, heels slightly apart. Transfer your weight to your heels, unlock your knees, and gently pull your heels towards each other. Stand tall, stretch your arms overhead, and press your fingertips together. Inhale, lifting your ribcage away from your hips. Exhale, tighten your core to support a 'lengthened' spine. Repeat until you feel energized and supported.

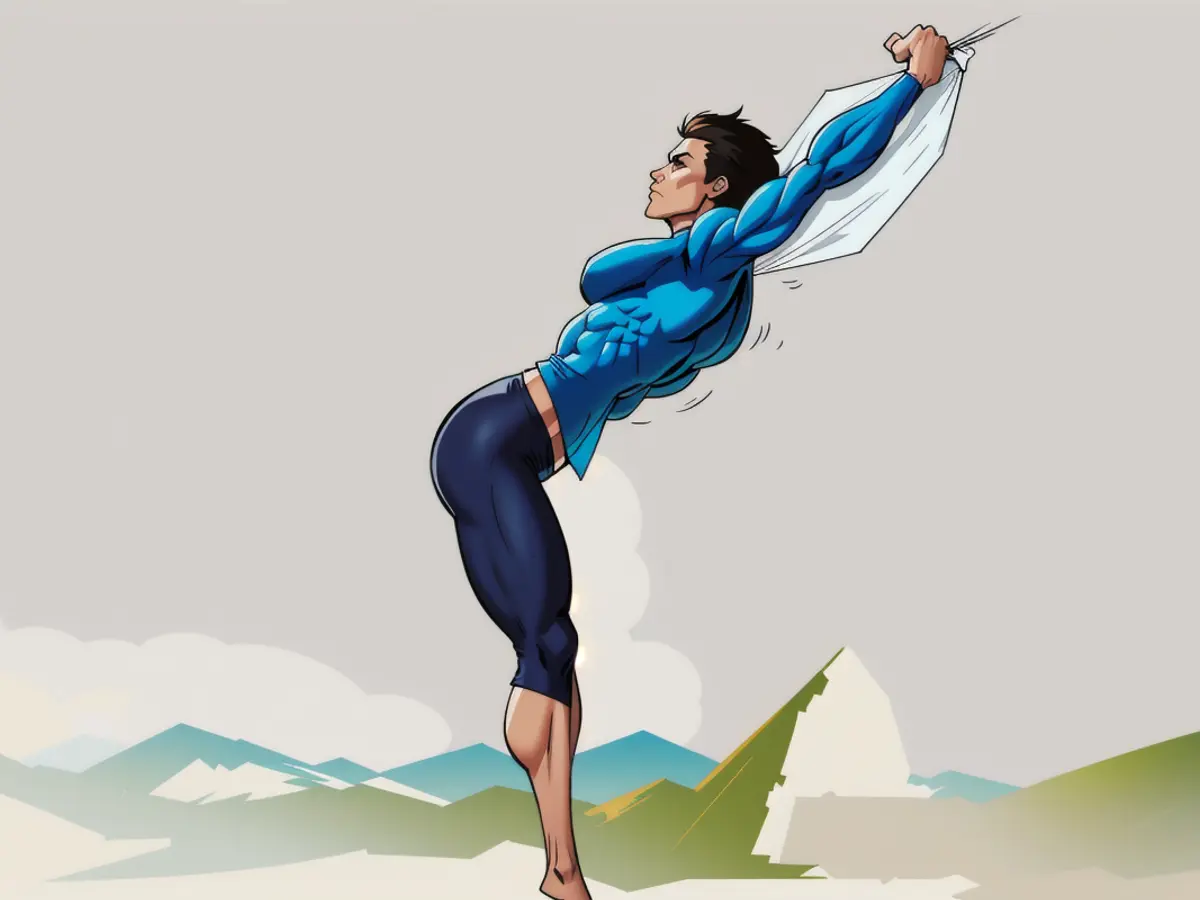
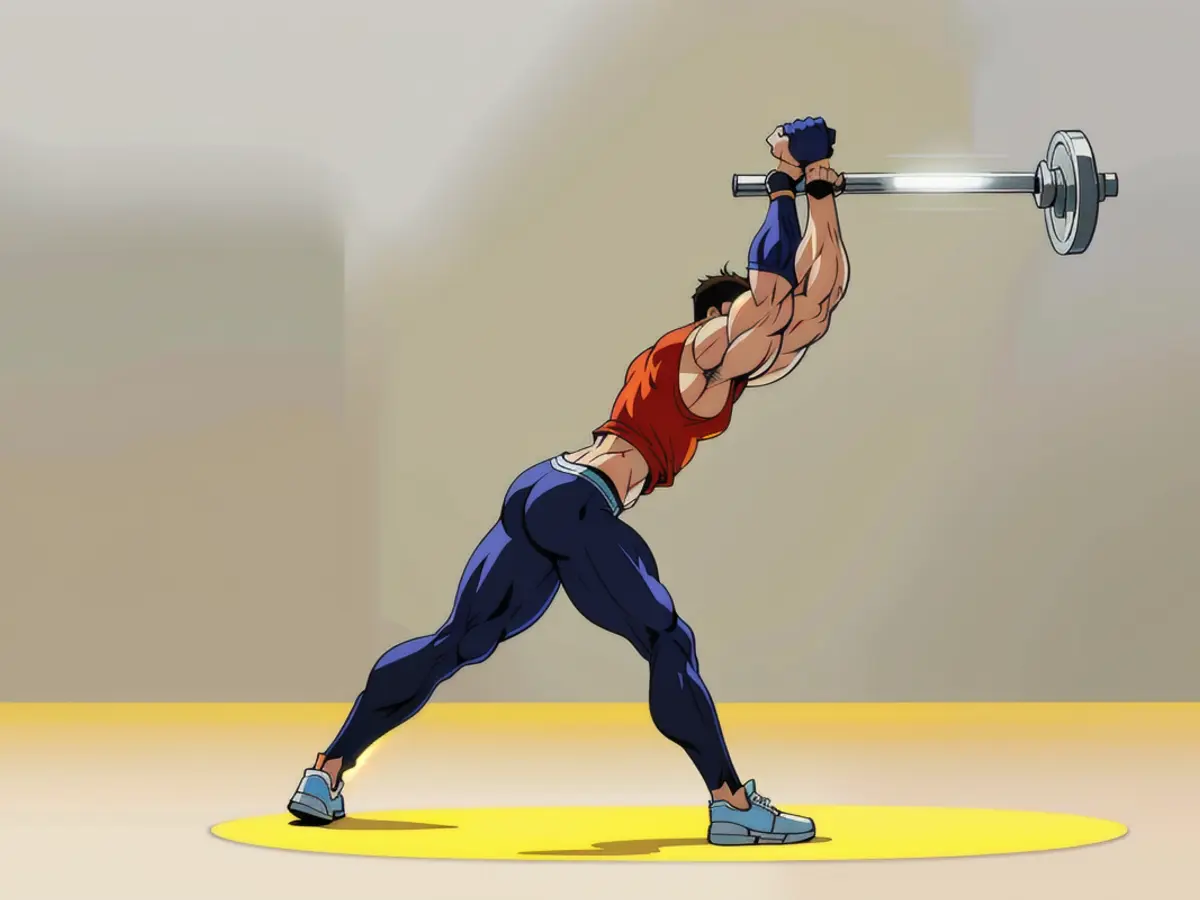
2. Modified Founder to Forward Fold
This move promotes integrated back and core strength, even if it seems a bit unusual. If a full founder puts too much tension on your lower back, try the modified version.
From the modified founder position, inhale and extend your arms in front of your heart, keeping your hips back and pressing your fingertips together. Slowly lift your arms, maintaining a neutral spine, and hold for 15-20 seconds.
From the full founder position, follow the instructions for the Forward Fold exercise, mentioned below. Make sure to keep your weight in your heels and maintain a neutral, stable spine to avoid strain on supporting structures.

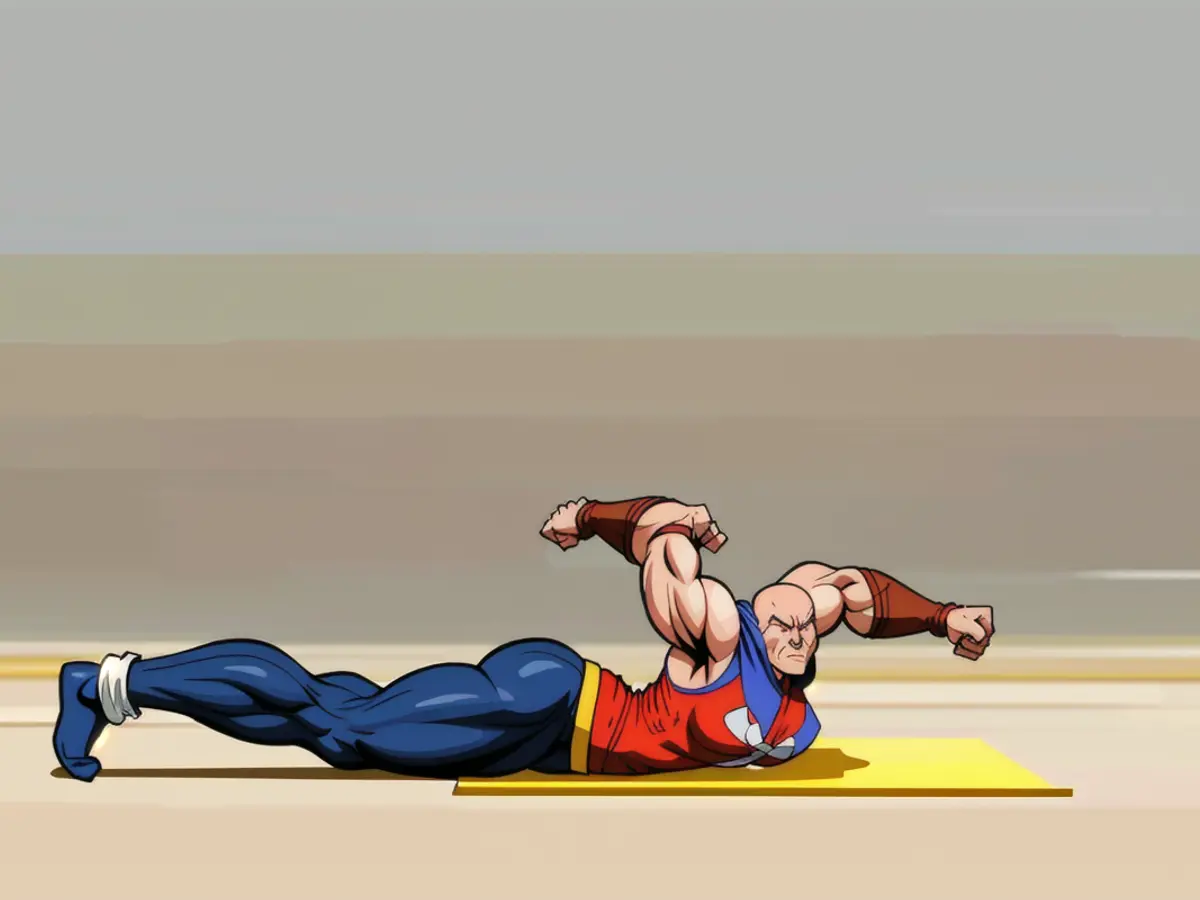
3. Adductor-Assisted Back Extension
This exercise isolates and strengthens deeper lower back muscles, with added support from the inner thighs.

Start by lying on your stomach with a slight knee bend. Press your hips and knees into the ground, lift your elbows, pull your shoulders down, and keep your neck in a neutral position. Hold the pose for 20-30 seconds.
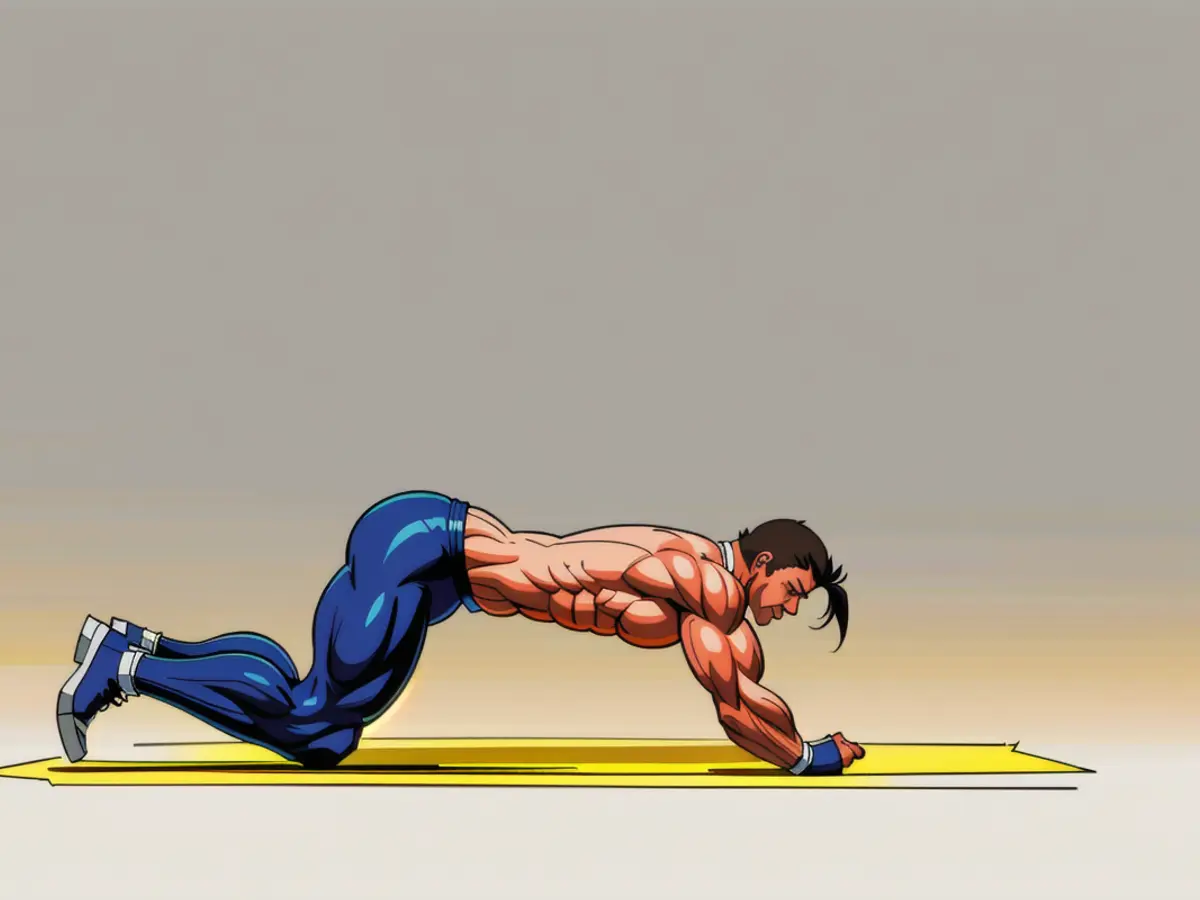
4. Eight-Point Plank
This plank variation targets your abs and core to support your spine.
Lie on your stomach with your feet flexed, knees touching, and elbows a few inches in front of your shoulders. Pull your shoulders away from your ears, and squeeze your knees and elbows towards your centerline. Lift your hips and maintain a neutral spine for 20-30 seconds.
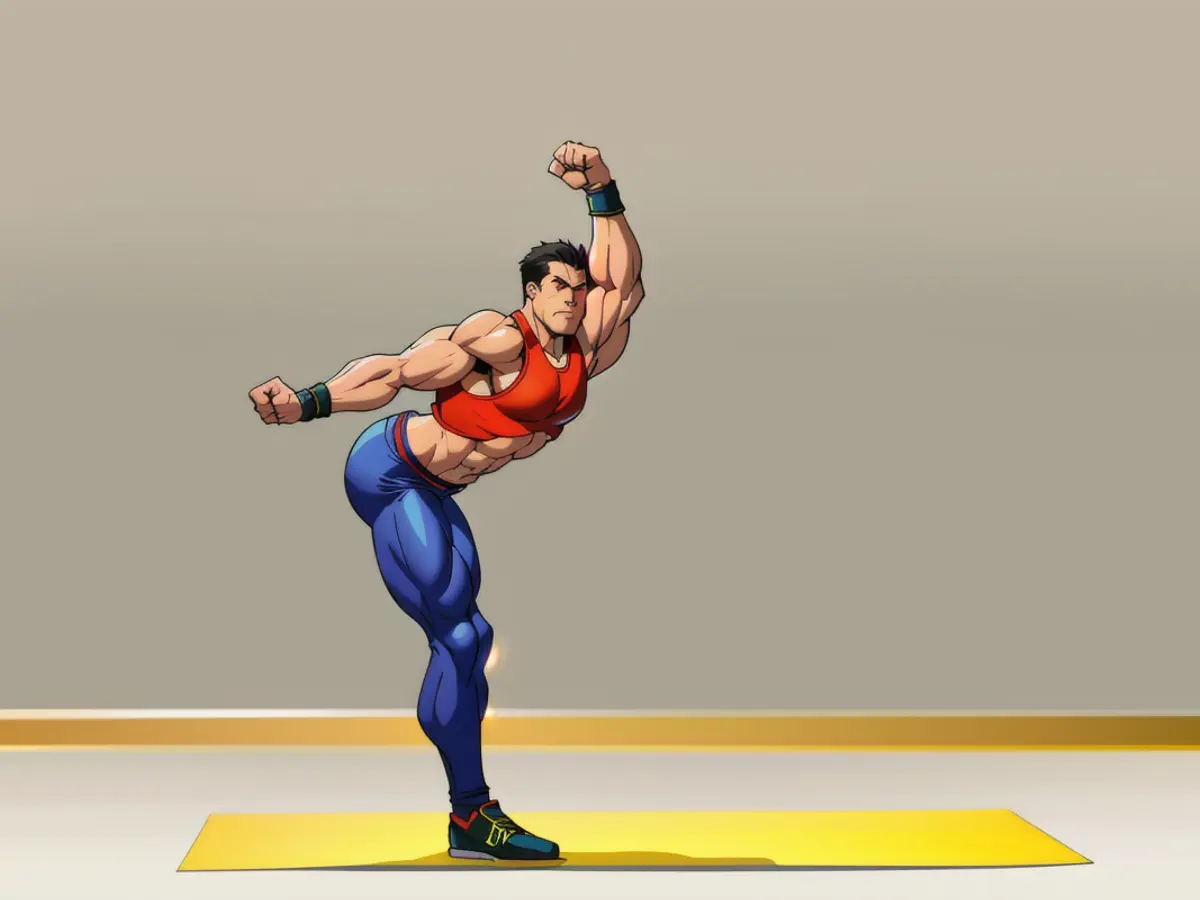
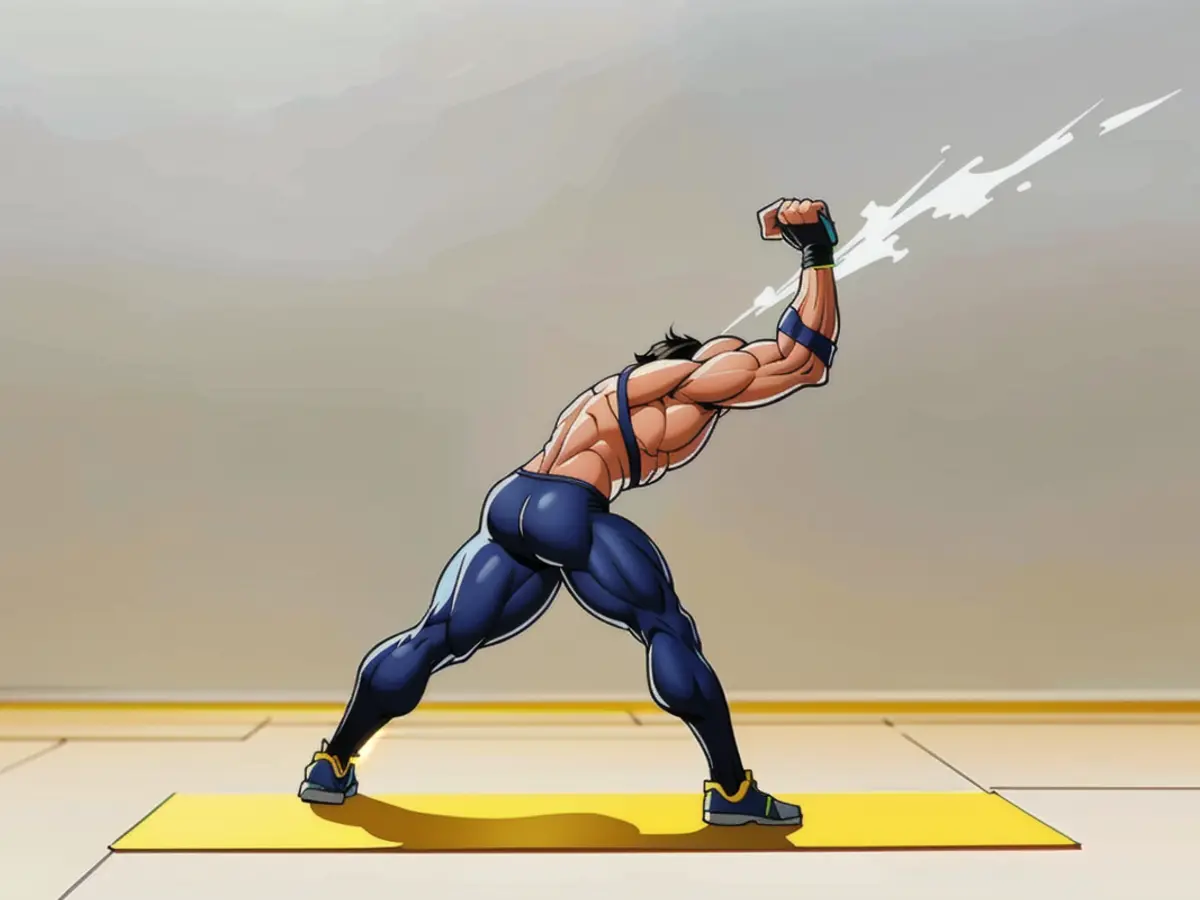
5. Mini Woodpecker
This move strengthens your butt muscles and back.
From a lunge position, press through your front heel and maintain a neutral spine. Keeping your arms extended, drive your butt back and stretch your hamstrings while maintaining a neutral spine. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then repeat on the other side.
Remember to consult a healthcare professional for a personalized exercise plan tailored to your needs and condition. Proper form and technique are crucial to maximizing benefits and minimizing injury risk.
Regular back-strengthening exercises are essential for weight management and avoiding upper back pain, as they help improve muscle weakness due to inactivity. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends performing these exercises two to three times a week, focusing on moves like diaphragmatic breathing, modified founder to forward fold, adductor-assisted back extension, eight-point plank, and mini woodpecker. These exercises not only strengthen your back and core but also promote spine strength and enhance oxygen intake.




