Throat Cancer and Laryngeal Cancer: Essential Facts
Throat cancers are a group of diseases that affect various parts of the throat, each with unique characteristics and symptoms. Here's a breakdown of four main types: laryngeal, hypopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, and nasopharyngeal cancers.
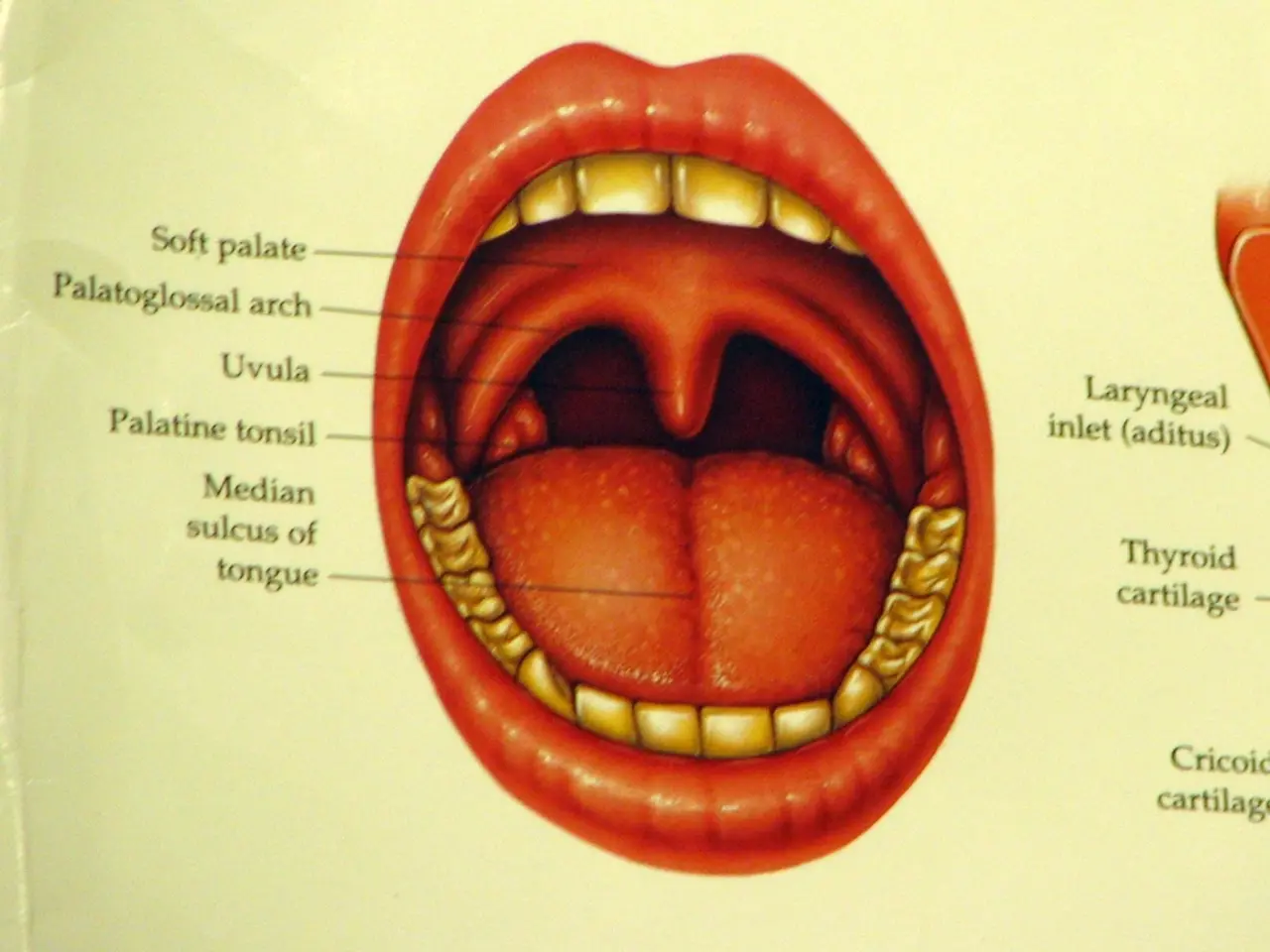
Laryngeal Cancer
Laryngeal cancer primarily affects the voice box, known as the "larynx." Symptoms often include persistent hoarseness or voice changes, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, ear pain, a lump in the neck, and breathing problems like shortness of breath or noisy breathing. It's important to note that laryngeal cancer may share symptoms with other conditions like benign tumors, but voice changes and hoarseness are particularly characteristic.
Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer starts in the lower part of the throat, behind and beside the larynx, and connects to the esophagus. Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing, throat pain, ear pain, and a possible neck lump.
Oropharyngeal Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is located in the middle part of the throat, including the base of the tongue, tonsils, soft palate, and pharyngeal walls. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing, persistent sore throat, throat or ear pain, and possibly a lump in the neck.
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer originates in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose. Symptoms include nasal congestion, nosebleeds, hearing loss or ringing in ears, headaches, and neck lumps due to lymph node involvement.
In the United States, hypopharyngeal cancers are less common than other types of throat cancer. SCCs in the larynx and hypopharynx are thin, flat cells that line these areas. The hypopharynx serves as the entrance to the esophagus, the tube connecting the mouth and stomach.
Persistent sore throat, ear pain, voice changes, hoarseness, pain when swallowing, difficulty swallowing, a lump in the back of the mouth, throat, or neck, coughing or spitting up blood are signs of throat cancer that should prompt a doctor visit.
HPV-related SCCs can occur following infection with certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV) and tend to have a better prognosis compared to HPV-negative SCCs. Squamous cell carcinomas are a subtype of throat cancer.
Nasopharyngeal cancer can cause difficulty breathing, hearing, or speaking. The most common early symptom of laryngeal cancer is vocal changes, such as a hoarse voice. Oropharyngeal cancers, like laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers, are primarily squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs).
Lymphomas are a type of cancer that can develop in the oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers, specifically in the tonsils and the base of the tongue. Sarcomas are rare cancers that can develop in the connective tissues of the larynx and hypopharynx, examples include chondrosarcomas and synovial sarcomas.
Laryngeal cancer can start in the supraglottis, glottis, or subglottis. Laryngeal cancer is a type of throat cancer that occurs in the voice box or "larynx." Oropharyngeal cancer occurs in the middle part of the throat, just behind the oral cavity.
Remember, persistent symptoms like sore throat, ear pain, and swallowing difficulties warrant medical evaluation to differentiate these conditions and their locations. Early detection and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for throat cancer patients. Always consult a healthcare professional if you experience any persistent or concerning symptoms.
Science has identified different types of throat cancers, each affecting distinct parts with unique symptoms. Oral cancers, particularly oropharyngeal cancers, often show symptoms such as persistent sore throat, ear pain, and difficulty swallowing, which are crucial signs that merit medical-health attention. Moreover, these health-and-wellness concerns underscore the importance of early-detection and prompt treatment to improve the prognosis for individuals dealing with these medical-conditions.