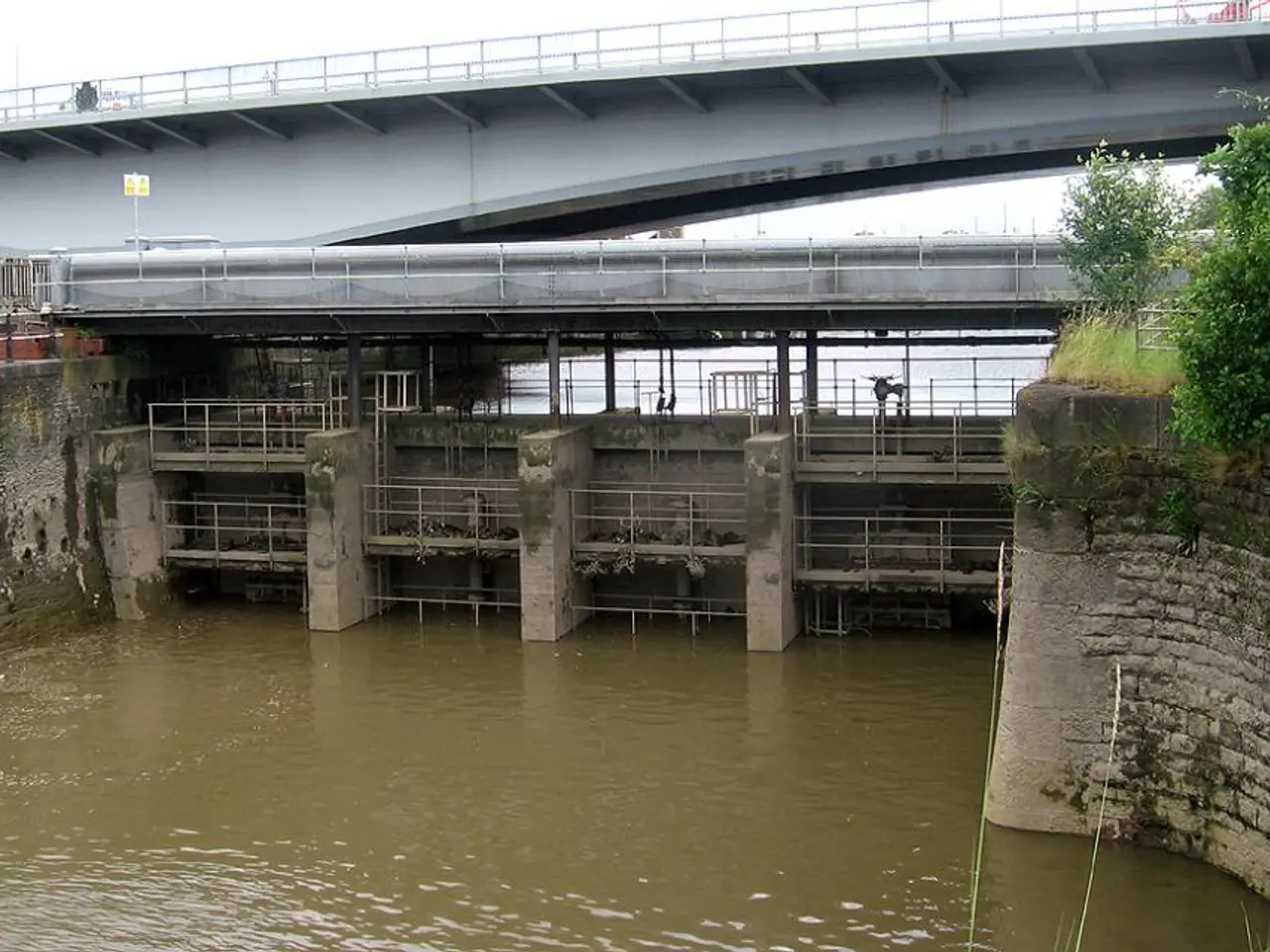
The durability of the flood barriers along the Rio Grande, specifically in El Paso, as they age gets brought into question.
In the heart of Texas, the aging levees along the Rio Grande in El Paso are undergoing a transformation as they face the challenges posed by climate change. These structures, designed to protect communities from devastating floods, have been a cornerstone of the region for centuries, shaping its cultural, economic, and environmental landscape [1].
The question of whether these levees can hold under the pressure of an uncertain future hinges on our collective commitment to addressing their vulnerabilities and ensuring their resilience. Fortunately, official Texas state plans confirm ongoing levee reinforcement efforts, with specific projects aimed at improvements along levees and detention ponds near El Paso [1]. Sites such as Levee Road 3 and detention pond Site 2, as well as enhancements around Rio Bravo Circle and Rio Grande Circle, are set to receive attention.
These efforts focus on improving levee infrastructure to better withstand future flooding events, a crucial need given the new variables introduced by climate change, such as increased rainfall intensity and frequency [2]. However, the technical specifications and extent of these flood control reinforcements remain to be seen.
Community members living along the Rio Grande can play a vital role in monitoring and reporting changes or potential issues with the levees, providing valuable early warnings [3]. Awareness among residents about the importance of levees and the risks of flooding can empower them to advocate for necessary improvements and support policy initiatives.
The Rio Grande, a river of significant historical importance, has demonstrated its power and unpredictability through past flood events. These reminders serve as lessons for engineers, policymakers, and communities about the need for continuous evaluation and adaptation of flood defenses [4].
The aging levees face numerous challenges, including erosion, sediment buildup, wear and tear, and the effects of climate change. Balancing flood control with environmental preservation is a complex challenge, and efforts to develop more environmentally friendly levee designs and management practices are ongoing [5].
Natural floodplain restoration can complement traditional levee systems by providing additional flood storage and reducing pressure on man-made structures [6]. Engineers are exploring solutions to address the vulnerabilities of aging levees, including reinforcement techniques, innovative materials, and advanced modeling and monitoring technologies [7].
In El Paso, the levees were constructed decades ago with technology and materials available at that time. Effective policy and adequate funding are essential to addressing the long-term challenges facing these structures [8]. The future of flood defense along the Rio Grande requires a multifaceted approach, including reinforcing existing levees, exploring alternative flood management strategies, and integrating engineering, policy, and community engagement.
References:
[1] Texas General Land Office Action Plan, July 2025. [2] Border wall construction activities near El Paso, various sources. [3] Engaging community members in monitoring and reporting. [4] Lessons from past flood events along the Rio Grande. [5] Balancing flood control with environmental preservation. [6] Natural floodplain restoration as a complement to traditional levee systems. [7] Exploring solutions to address the vulnerabilities of aging levees. [8] Effective policy and adequate funding for levee upgrades.
- The transformation of the aging levees in El Paso, Texas, is a pressing issue amidst climate change, as their resilience relies on science-based research and policy-and-legislation commitments.
- The evolution of levee infrastructure in the region is critical to address the challenges posed by climate change, such as increased rainfall intensity and frequency, within the context of environmental-science.
- The role of community members living along the Rio Grande is significant in monitoring levees for changes or potential issues, contributing to health-and-wellness and general-news awareness about the importance of flood defenses.
- The environmental-science community is striving to balance flood control with ecosystems preservation, working on more environmentally friendly levee designs and management practices.
- Natural floodplain restoration can be a valuable addition to traditional levee systems, providing extra flood storage and reducing pressure on man-made structures, all while promoting environmental-science and policy-and-legislation.
- Innovations in engineering, such as reinforcement techniques, novel materials, and advanced modeling and monitoring technologies, are crucial for addressing the vulnerabilities of aging levees and adapting to climate change.