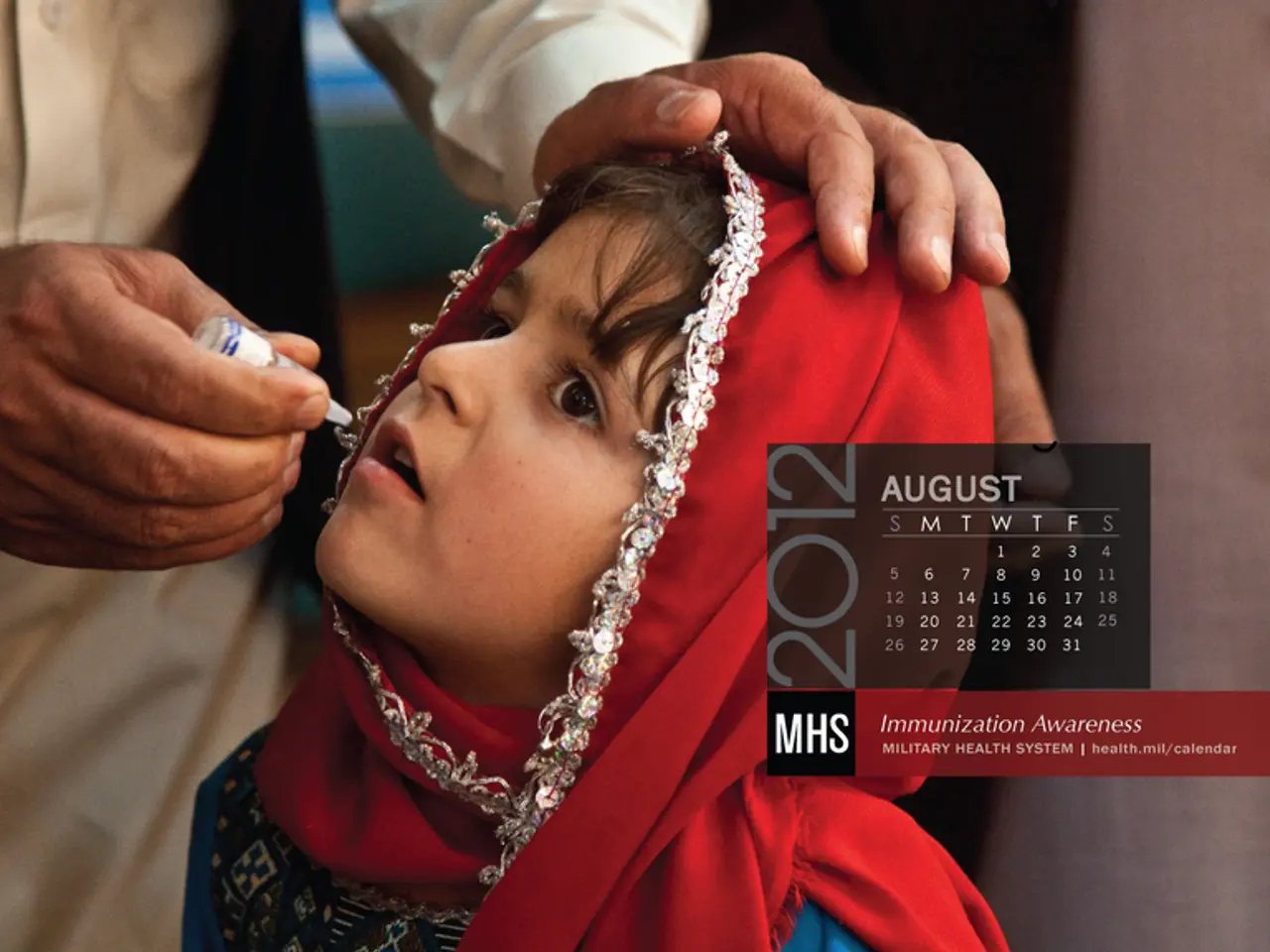
Vaccination Progress for Children in Danger: A Worldwide Conundrum
Global Vaccination Rates for Deadly Childhood Diseases Halt Amidst Widespread Decline - Global Progress on Child Vaccinations Against Life-Threatening Illnesses Has Stagnated
The modern era has seen a shocking halt in life-saving child vaccinations across the globe, a concerning development that could potentially trigger outbreaks of preventable diseases, according to researchers. This setback has been further magnified by drastic cuts in international aid, potentially reversing gains made in child vaccination for decades.
An international team of researchers scrutinized vaccination rates in over 200 nations between 1980 and 2023 for this study. Despite the grim outlook, the researchers acknowledged some promising strides. An immunization program led by the World Health Organization (WHO) has an estimated 154 million lives since the mid-1970s. Over the same period, the vaccination rate for diseases like diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, measles, polio, and tuberculosis has more than doubled.
However, these encouraging signs seem to be on a declining trajectory. The pace of improvement slowed in the 2010s, with measles vaccinations dropping in around half of the researched countries. The most substantial decline was observed in Latin America. In more than half of high-income countries, the proportion of children receiving at least one dose of vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, measles, polio, or tuberculosis also decreased.
The COVID-19 pandemic then arrived, causing disruptions to regular vaccinations. These disruptions forced an additional 13 million children to remain unvaccinated between 2020 and 2023. Currently, approximately 15.6 million children have missed the full three-dose vaccination schedule for diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, or measles.
The gap in vaccine access remains considerable, particularly in poorer nations. Over half of the 15.7 million unvaccinated children globally in 2023 reside in eight countries, mainly south of the Sahara in Africa.
In the European Union, the number of measles cases has surged by ten times in the past year alone, while the US recently witnessed over a thousand measles cases in 30 states, exceeding the total recorded in 2023. Reports of polio, once eradicated in many regions, are rising in Pakistan and Afghanistan. Presently, Papua New Guinea is experiencing a polio outbreak.
"Childhood vaccinations represent one of the most powerful and cost-effective public health measures," explained Jonathan Mosser, a lead author from the US Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). "Prolonged global inequalities, the COVID-19 pandemic challenges, misinformation, and growing vaccine skepticism have combined forces to halt the immunization process," Mosser added.
Other contributing factors include increasing displacement numbers due to armed conflicts, political instability, economic uncertainty, and climate crises, notes Emely Haeuser, another lead author from IHME.
Scientists warned that these backsteps could jeopardize the WHO's objective of vaccinating 90% of all children and adolescents worldwide by 2030, an ambitious target also aimed at halving the number of unvaccinated children compared to 2019 by 2030. As of now, only 18 countries have achieved this goal, according to the study, backed by the Vaccine Alliance, Gavi, and the Gates Foundation.
The global healthcare system has faced tumultuous times since the U.S. government drastically reduced international aid under the Donald Trump Administration. "For the first time in decades, the number of child deaths worldwide is more likely to increase rather than decrease due to drastic reductions in foreign aid," said Bill Gates. "This is a tragedy," added the Microsoft co-founder. At the Gavi vaccine alliance's donor conference in Brussels, Gates pledged 1.6 billion dollars (around 1.4 billion euros).
- Child Health
- Vaccines
- COVID-19 Pandemic
- WHO
- Healthcare Access
- Inequality
- Measles
- Polio
- Bill Gates
- South Africa
- Climate Crisis
- Displacement
- Political Unrest
- Economic Instability
Additional Insights:
- Systematic tracking of a child's immunization history is crucial for early identification of missed doses and informed decision-making.
- AI and smart public health tools are increasingly recognized as vital in improving vaccine coverage and ensuring no child is overlooked.
- Behavior change interventions informed by models like the COM-B are essential in addressing vaccination hesitancy and access issues.
- The factors contributing to the decline in child vaccination rates are wide-ranging, encompassing healthcare system limitations, socio-behavioral factors, and emerging global health challenges. Latin America experiences additional complications due to regional disparities, socio-economic inequalities, and Health crises.
- The slowdown in child vaccination progression, initially identified in the 2010s, is a concerning development in over 200 nations.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has been instrumental in saving an estimated 154 million lives since the mid-1970s through an immunization program.
- Vaccination rates for diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, measles, polio, and tuberculosis have more than doubled since 1980.
- However, the pace of improvement has slowed, with measles vaccinations decreasing in around half of the researched countries.
- The most substantial decline was observed in Latin America, where the number of children vaccinated also decreased.
- Over half of high-income countries have seen a decline in the proportion of children receiving vaccines for diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, measles, polio, or tuberculosis.
- The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted regular vaccinations, causing an additional 13 million children to go unvaccinated between 2020 and 2023.
- Currently, approximately 15.6 million children remain unvaccinated, having missed the full three-dose vaccination schedule for diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, or measles.
- Over half of the 15.7 million unvaccinated children globally reside in eight countries, mainly in Africa south of the Sahara.
- In the European Union, measles cases have surged tenfold in the last year, while the US has witnessed over a thousand cases across 30 states.
- Reports of polio, once eradicated in many regions, are rising in Pakistan and Afghanistan, and Papua New Guinea is currently experiencing a polio outbreak.
- Childhood vaccinations are one of the most powerful and cost-effective public health measures, but prolonged global inequalities, the COVID-19 pandemic, misinformation, and growing vaccine skepticism have halted the immunization process.
- Scientists warn that these setbacks could jeopardize the WHO's objective of vaccinating 90% of all children and adolescents worldwide by 2030.
- The global healthcare system has faced challenges since the U.S. government drastically reduced international aid under the Donald Trump Administration.
- Bill Gates, a Microsoft co-founder, has expressed concern that the number of child deaths worldwide is more likely to increase rather than decrease due to drastic reductions in foreign aid.
- Climate crises, displacement, political instability, and economic uncertainty are contributing factors to the decline in child vaccination rates.
- Systematic tracking of a child's immunization history is essential for early identification of missed doses and informed decision-making.
- AI and smart public health tools are increasingly recognized as vital in improving vaccine coverage and ensuring no child is overlooked.
- Behavior change interventions informed by models like the COM-B are essential in addressing vaccination hesitancy and access issues.
- Latin America faces additional complications due to regional disparities, socio-economic inequalities, and health crises that contribute to the decline in child vaccination rates.
- Child health, vaccines, and the worldwide conundrum of stagnating child vaccinations are significant topics in the science and healthcare policy spheres.
- Climate change and its impacts on public health policy are issues of concern in environmental science.
- The manufacturing industry plays a critical role in the production and distribution of vaccines.
- Renewable energy and its implementation in the energy sector can help combat climate change, reducing carbon emissions.
- Mental health is a crucial aspect of overall health and wellness, andAddressing mental health issues in the workplace through workplace-wellness programs is an important aspect of men's health and social policy.
- Fitness and exercise have numerous health benefits, including improving cardiovascular health and managing weight.
- Sexual health education and resources are essential for promoting prevention and early detection of sexually transmitted inquiries.
- Autoimmune disorders, neurological disorders, and skin conditions are conditions that require specific therapies and treatments for management and treatment.