Anti-Inflammatory Diets May Help Manage Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
Ulcerative colitis (UC), a type of inflammatory bowel disease, can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. While medications like aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants are the primary treatments, an anti-inflammatory diet may also help alleviate symptoms.
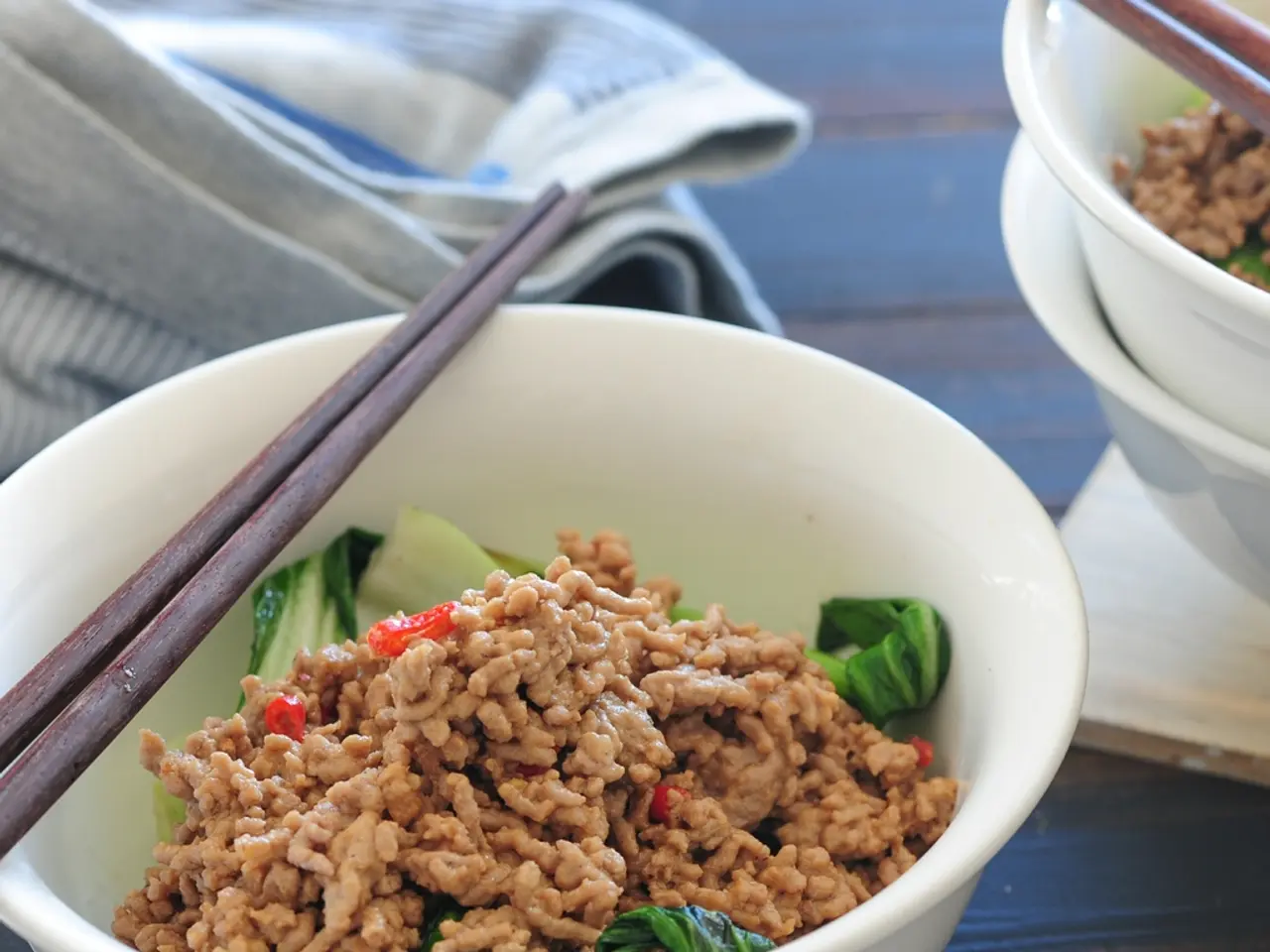
Anti-inflammatory diets, such as the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD) and the Mediterranean diet, focus on whole, unprocessed foods and may lower inflammation and modulate the gut microbiome. Olive oil, a key component of the Mediterranean diet, has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects. However, fiber intake in UC has mixed effects, with soluble fiber potentially being better tolerated than insoluble fiber. It's crucial to note that ultra-processed foods, excess sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can worsen UC symptoms. Additionally, carrageenan, a common food additive, may exacerbate UC symptoms. Red meat, poultry, and processed meat intake may also be linked to UC development. Fermented foods like yogurt or kefir, on the other hand, may help UC by supporting gut microbiome diversity.
While anti-inflammatory diets may help manage UC symptoms, it's essential to discuss any new diet with a healthcare professional. The Mediterranean diet, rich in plant foods and olive oil, and the SCD, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, may be beneficial. However, individual tolerance to fiber and specific foods may vary, and professional guidance is recommended.